Computers are made to run tasks for you in order to let you get your work done more quickly and efficiently. But there may be times when you need to manage these tasks to see what’s going on or diagnose a problem with your computer. This is where the Windows Task Manager comes in.
The purpose of the Windows Task Manager is to give you a way to see what is running on your computer at any given time. This includes open programs and processes/services. You can also check the performance of your computer in respect to RAM and CPU usage plus network utilization which can help you diagnose performance issues and find the cause.
There are other things you can do with Task Manager that most people will never have the need to do. Such things include changing the priority of a process, assigning a process to a processor if you have a multiprocessor system and starting a new program. Not all of these features are available in every version of Windows.
To get to the Windows Task Manager press Ctrl+Alt+Del on your keyboard and then choose task Manager or right click on a blank spot of your Taskbar and choose Start Task Manager.
Here you can see the older Windows 98 version of Task Manager.
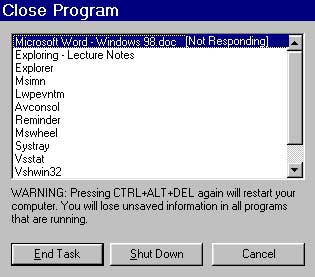
As you can see you don’t have many options here. You can mainly use this version to end a task/program or to shut down the computer.
The Windows 2000 and up versions have many more features to manage your tasks.
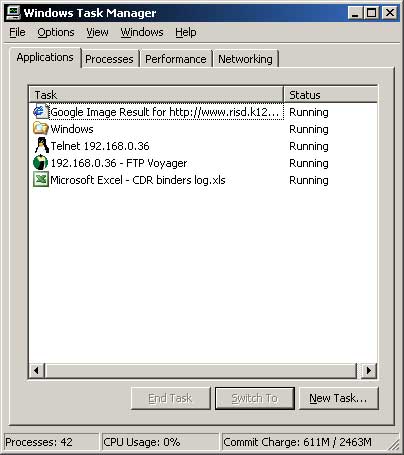
On the Applications tab you can view the running tasks, end a task, start a new task or switch from task to task. You can right click on an application and choose Go to Process and Task Manager will take you to the process associated with that task in case ending the application doesn’t work and you want to end the process instead.
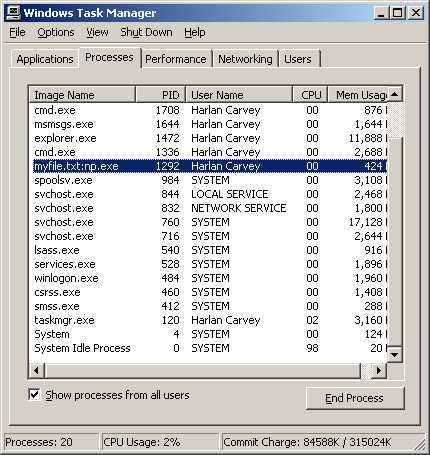
On the Processes tab you can view all the running processes and end any that may be giving your trouble. Keep in mind that ending the wrong process can cause undesirable results.
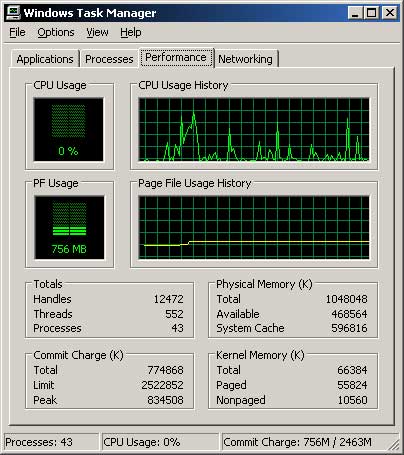
The Performance tab allows you to check the current memory, CPU and pagefile usage. If you suspect a certain application is using a lot of resources then you can confirm this here.
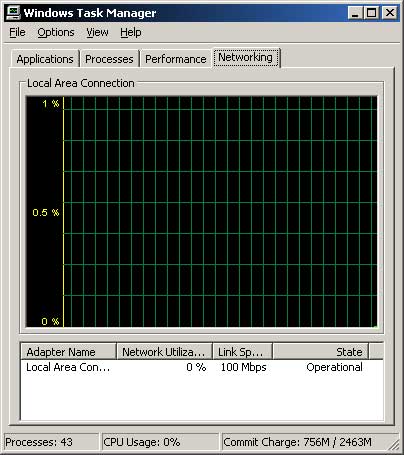
The Networking tab allows you to check your network resources if you are on a network. It will list the available adapters, the percentage of bandwidth it is using, the speed of the link and what state it is in.
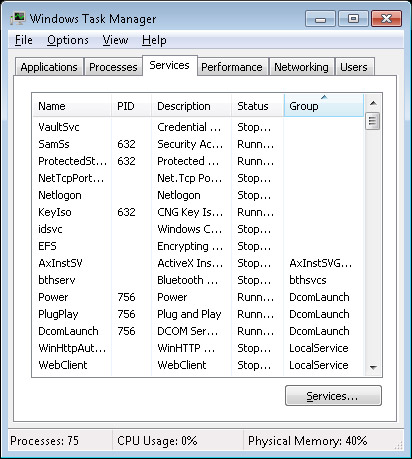
Windows Vista and up have a Services tab where you can start and stop services as well as find the process associated with that particular service. Services can also be manged with the Services management console by clicking on Start and typing in services.msc in the Run box or Search box.